I came across HMAC (Hash-based message authentication code) functions when developing a RESTful client application in Delphi. The RESTful Web Service API required me to send HMAC_SHA256 signatures (Base64 encoded) with each HTTP request.
HMAC functions take two parameters: a key and a message. The purpose of the HMAC function is to authenticate the message and guarantee the data integrity of the message.
The cryptographic strength of the HMAC function lies on the underlying hashing function that it uses: MD5, SHA1, SHA256, etc.
So, these functions are usually are termed HMAC_SHA256, HMAC_SHA1, HMAC_MD5 to connote the core hashing function being used.
The outcome of a HMAC function is basically an array of bytes, but it is usually represented as a hexadecimal string or encoded as a Base64 string. (The RESTful Web Service API needed the Base64 encoded output).
I Googled around for a bit, but I didn’t get a clean implementation of HMAC_SHA256 in Delphi (encoded as Base64). I glued together the pieces from some questions on StackOverflow and coded an Indy based implementation that uses generics to specify the core hashing function.
Brief description: I created a helper class called THMACUtils. Note that this class uses generics to indicate the hashing algorithm (TIdHMACSHA256, TIdHMACSHA1). Three functions are provided: the main thing happens in the HMAC(...) function; HMAC_HexStr(...) and HMAC_Base64(...) are simply decorations of the output.
unit HMAC;
interface
uses System.SysUtils, EncdDecd, IdHMAC, IdSSLOpenSSL, IdHash;
type THMACUtils<T: TIdHMAC, constructor> = class public class function HMAC(aKey, aMessage: RawByteString): TBytes; class function HMAC_HexStr(aKey, aMessage: RawByteString): RawByteString; class function HMAC_Base64(aKey, aMessage: RawByteString): RawByteString; end;
implementation
class function THMACUtils<T>.HMAC(aKey, aMessage: RawByteString): TBytes;var _HMAC: T;begin if not IdSSLOpenSSL.LoadOpenSSLLibrary then Exit; _HMAC:= T.Create; try _HMAC.Key := BytesOf(aKey); Result:= _HMAC.HashValue(BytesOf(aMessage)); finally _HMAC.Free; end;end;
class function THMACUtils<T>.HMAC_HexStr(aKey, aMessage: RawByteString): RawByteString;var I: Byte;begin Result:= '0x'; for I in HMAC(aKey, aMessage) do Result:= Result + IntToHex(I, 2);end;
class function THMACUtils<T>.HMAC_Base64(aKey, aMessage: RawByteString): RawByteString;var _HMAC: TBytes;begin _HMAC:= HMAC(aKey, aMessage); Result:= EncodeBase64(_HMAC, Length(_HMAC));end;
end.
Below there’s an example of how to use the THMACUtils class.
program HMACSample;
{$APPTYPE CONSOLE}
{$R *.res}
uses
System.SysUtils,
HMAC,
IdHMACSHA1,
IdHashMessageDigest;
begin
try
Write('HMAC_SHA1("key", "message")'#9#9'= ');
Writeln(THMACUtils<TIdHMACSHA1>.HMAC_HexStr('key', 'message' ));
Writeln;
Write('HMAC_SHA256("key", "message")'#9#9'= ');
Writeln(THMACUtils<TIdHMACSHA256>.HMAC_HexStr('key', 'message' ));
Writeln;
Write('HMAC_SHA1_Base64("key", "message")'#9'= ');
Writeln(THMACUtils<TIdHMACSHA1>.HMAC_Base64('key', 'message' ));
Writeln;
Write('HMAC_SHA256_Base64("key", "message")'#9'= ');
Writeln(THMACUtils<TIdHMACSHA256>.HMAC_Base64('key', 'message' ));
Readln;
except
on E: Exception do
Writeln(E.ClassName, ': ', E.Message);
end;
end.The console application above looks like this:
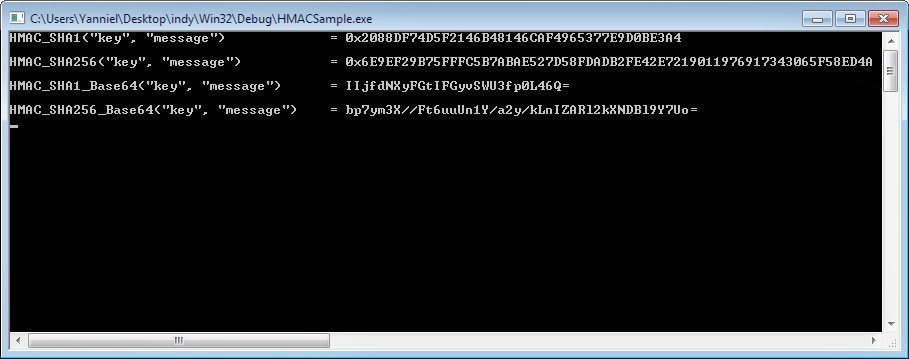 |
| HMAC Sample Application Delphi |